Guide: Using Calendly with Databox (Custom API Integration)
IN THIS ARTICLE
- Calendly Integration Details
- How to Connect Calendly to Databox
- How to Use and Create Calendly Metrics
- Additional Information
Calendly Integration Details
IN THIS SECTION
Overview
Calendly is a powerful scheduling software for organizing meetings and appointments between individuals and their colleagues, and between organizations and their clients or customers
The Calendly integration is designed for more tech-savvy users, as it syncs data through a Custom API integration. In order to create Calendly metrics in Databox, you’ll need to use the Metric Builder. Learn more about the basics of Metric Builder for Custom API Integrations here.
Custom API Integrations are available on Professional and higher plans. Request a trial of Metric Builder by following these steps.
If you'd like us to help you get set up with Calendly in Databox, please fill out this request form or book a call with one of our product experts:
- Free Databox users (or potential users) book a call here
- Paying Databox customers book a call here
Integration basics
| Integration status | Beta |
| Type of Account access needed | Basic (depends on endpoints) |
| Authorization type | OAuth2 |
| Available endpoints | All REST endpoints |
| Available requests | All GET requests |
| Needed permissions (scopes) | default |
| Allowed API versions | All currently active API versions. Example: You can use a v1 of an API or v4, as long as they are both still supported. Deprecated APIs normally stop returning data. |
| Timezone | User's timezone |
| Dynamic date range support | No |
| Pagination support | Yes |
| Type of Pagination supported | Next type |
| Rate Limits | Yes |
| Official documentation | https://developer.calendly.com/api-docs/4b402d5ab3edd-calendly-developer |
| Follow the status of the API on the official changelog | https://www.calendlystatus.com/ |
How to connect Calendly to Databox
IN THIS SECTION
- What’s the maximum amount of historical data initially available when you use a new Calendly Metric in Databox?
- What time zone does Calendly data sync in?
- What type of pagination is supported by Calendly Integration
How to connect Calendly to Databox
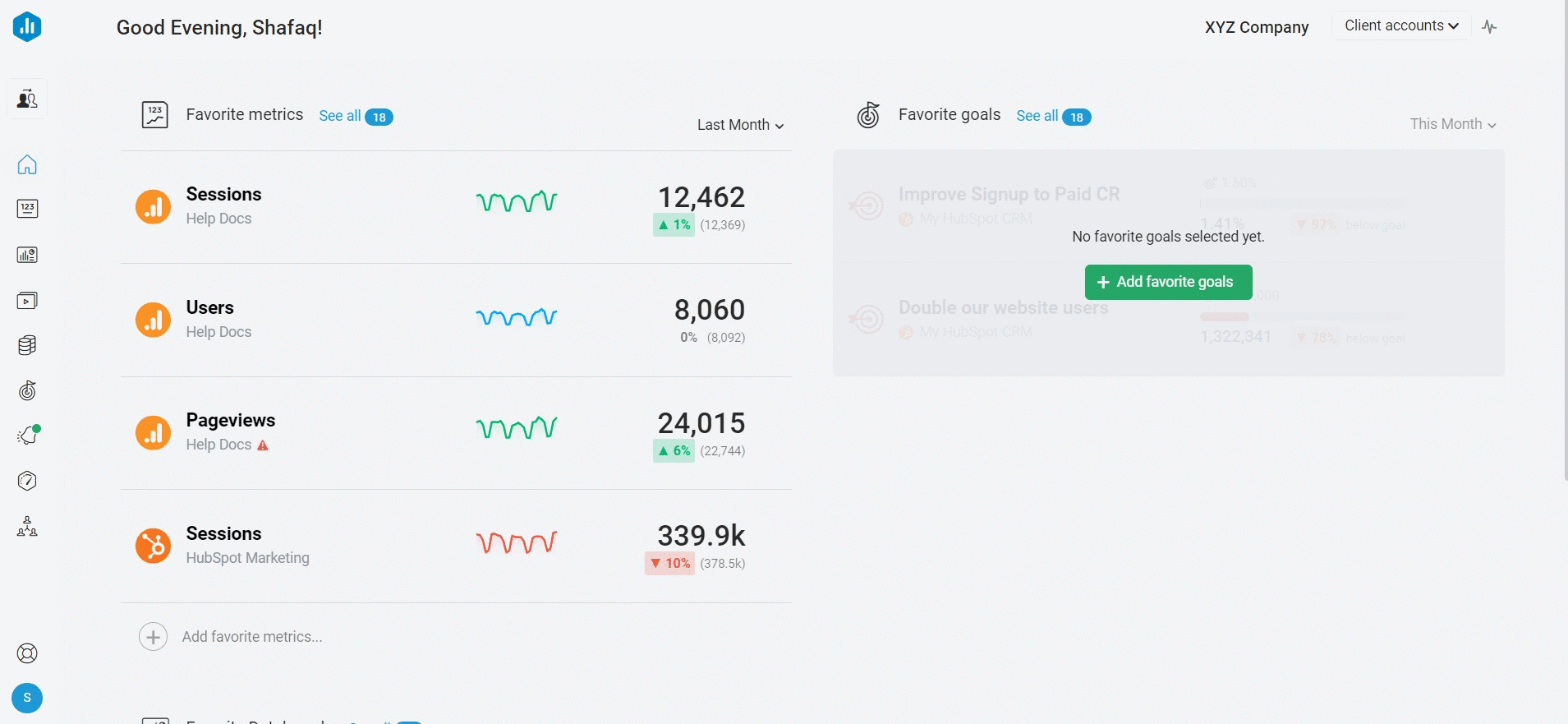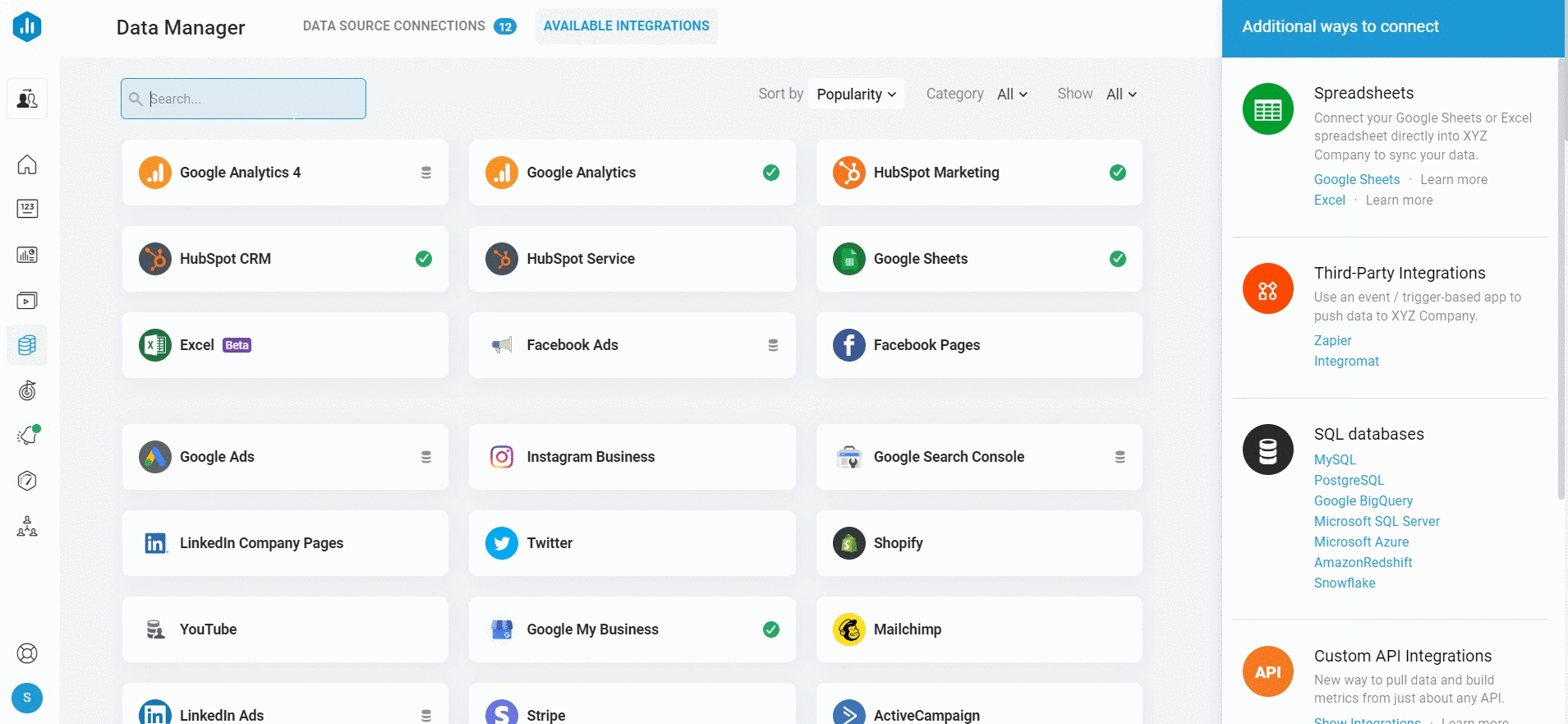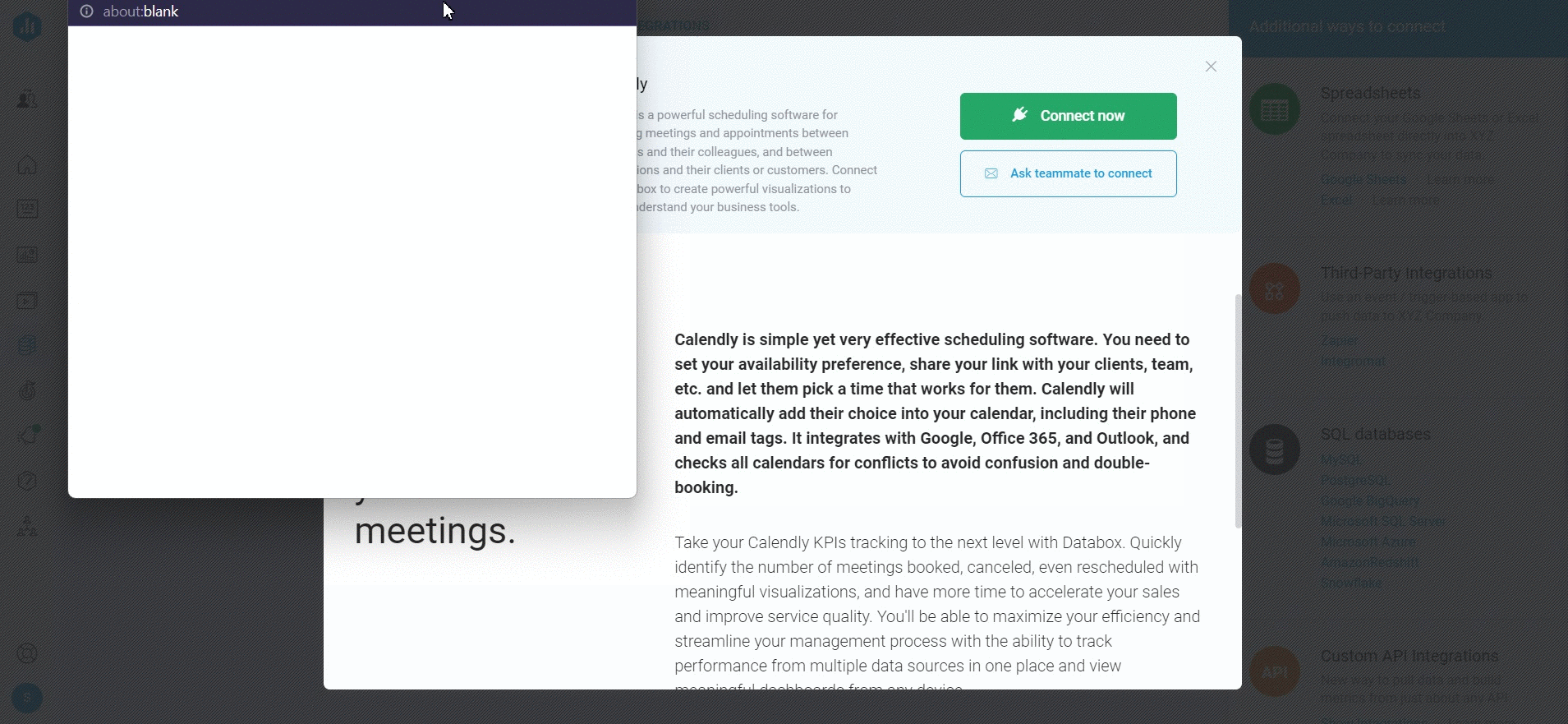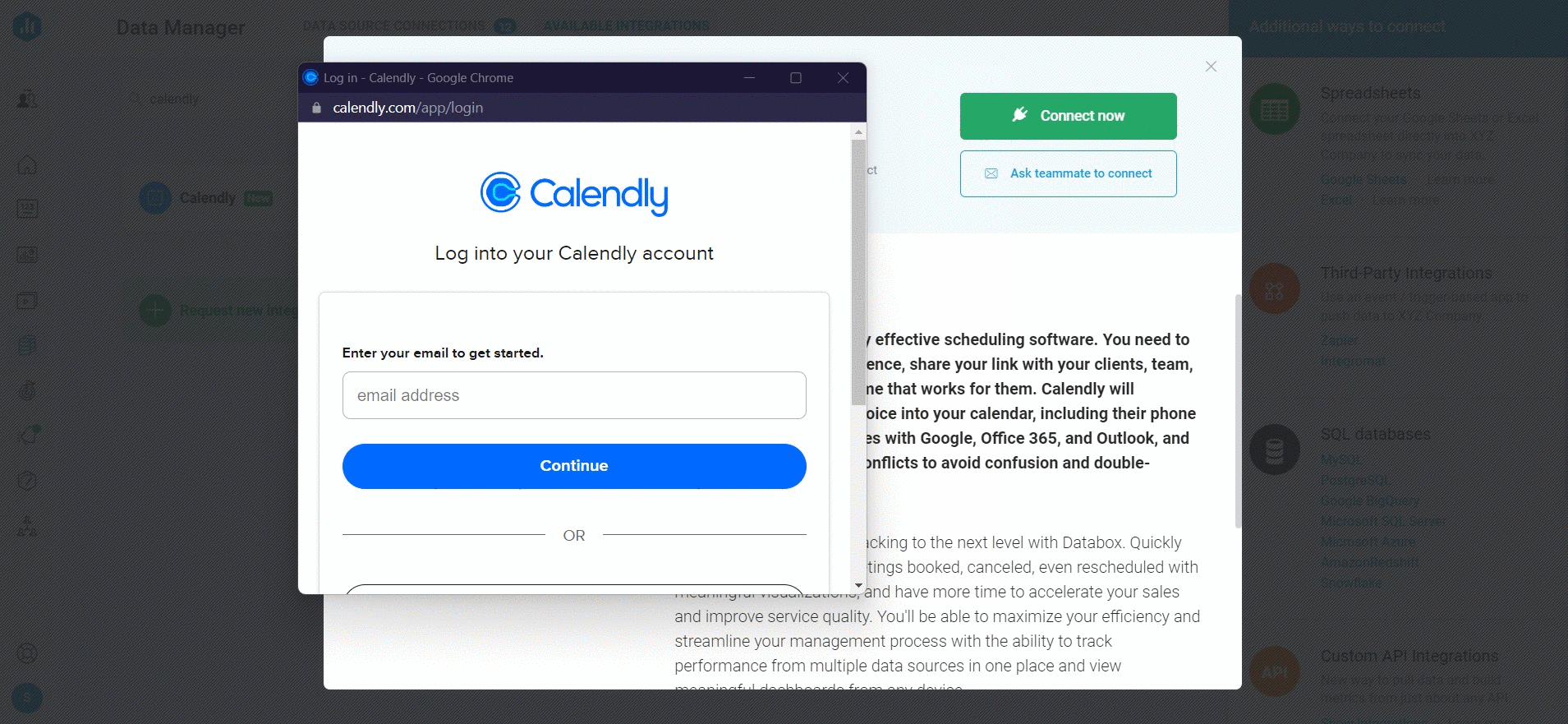
To connect a Calendly Account in Databox, go to Data Manager > + New connection. Type Calendly in the search bar and click on the Connect button. Next, click the green Connect now button.
This will open the Authorization window, where you will be prompted to enter your Calendly login credentials and authorize the Databox app
What's the maximum amount of historical data initially available when you use a new Calendly Data Source Metric in Databox?
The amount of historical data available in Databox is dependent on the custom metric setup, API limitations, pagination limitations, and the user’s Databox plan:- Custom Metric Setup: When a user creates a metric using an endpoint that supports date time parameters in the API request, those date time parameters determine the amount of historical data that will be pulled for the given metric. You can learn more about the date time parameters here.
- API Limitations: APIs may have limits set by the system itself on the amount of historical data that is stored/ can be accessed.
- Pagination Limitations: The pagination limit is set to 100 pages, which means that pagination will stop when the 100th page is reached. In cases where the metric is using pagination, of course, the interplay of date time parameters and pagination can have an impact on how much of the historical data the user can pull for a given metric. Learn more here.
- Databox Plan: The amount of historical data you're able to access in Databox is dependent on your Databox plan. Learn more here.
Pro Tip: In order to start syncing data for a Metric, you can add it to your Metrics screen, use it in a Scorecard, set a Goal around it, create an Alert for it, or add it to a Databoard. Learn more here.
What time zone does Calendly data sync in?
Calendly's data is synced in the time zone set in the Calendly Account For example, if the Calendly Account time zone is set as EST, the C data will sync with Databox in EST?
What type of pagination is supported by Calendly Integration
The pagination limit is set to 100 pages, which means pagination will stop when the 100th page is reached. We recommend you use the maxResults parameter. This parameter will increase the default number of records returned (maximum 500, default is 100). The default number of elements returned is 20 and can be set to a maximum of 100.
Learn more about pagination here
How to create custom Calendly Metrics
Let’s walk through how to create a Custom Metric for Calendly.
In order to prepare API requests, you should reference API-specific documentation that can be found in the Databox app through the API Docs link in the top right of the Prepare API Request page. Or, use this direct link.
- Navigate to Metrics > Custom Metrics to access the Metric Builder for Calendly.
- Click the green + New Custom Metric button and select your connected Calendly Account from the Data Source drop-down list.
- Open the API documentation for Calendly to find the endpoint that will return the data needed for the given custom metric you wish to create.
- Click the drop-down to select GET or POST as the HTTP Method. This is dependent on the information you found in the API documentation.
- The Base URL is already predefined, you will need to copy the missing part of your chosen endpoint to sync the appropriate data.
-
Add Parameters based on your HTTP Method. Parameters limit the records returned for the API request.
-
If you’re creating a GET request, define the Key and Value pair(s). The API documentation provides information on endpoints for a field/ argument, which will be the Key. The condition (i.e., an ID, true/ false, etc.) will be the Value.
If the API documentation for Calendly states that the Integration supports dynamic date ranges, you will be able to click the calendar icon to add datetime parameters. -
If you’re creating a POST request, define the relevant JSON body.
Click on the calendar icon to add datetime parameters. - Pro Tip: You can choose multiple Keys and Values for one Custom Metric. You can add an additional Key and Value by clicking on “+”.
-
- You can add Headers that include Key and Value pairs if the API needs this to successfully return data.
- If the endpoint supports pagination, we recommend you select the appropriate method using the Pagination Method dropdown.
- Once you have the basic setup, click on the green Continue button. You will be directed to the Select value step.
- In the Select value step, select a property that includes the metric value you'd like to track in your Custom Metric. A metric value must be purely numeric.
- Once you have selected the value, click on the green Continue button.
-
The Segment by dimension step is optional. This step will be taken into account only when you are trying to create a dimensional metric. If you'd like to segment your metric by multiple dimensions, choose one to complete during this set up, then begin again and select a different dimension until each desired metric is created.
-
To skip this step, select None.
-
- The Select date step is optional as well.
- Use current time of storing data (Dynamic): Select this option if you don’t want to select a date field
- Use a field from response (optional): Select this if you want to select a date in order to see your data in predefined intervals.
- In the Preview & Customize step, you can see the JSONata expression that has been created based on your selection of properties.
-
You can customize the JSONata expression (optional) in the right editor panel.
-
- To continue, click on the Preview data button to validate the expression and returned data.
- Once you have previewed your data, click on the green Continue button to proceed to the last step of setting up your Custom Metric.
-
In the Describe metric step, you can set up the following:
-
Name your metric: Enter a name for your custom metric.
-
Data Aggregation: These selections determine how your data is handled. This especially impacts the way data is grouped and displayed for longer Date Ranges. Learn more here.
-
Favourable trend: You can select when "Trending UP is positive" or "Trending DOWN is positive," since some metrics are better (positive) when the value is lower (like Bounce rate, Churn rate, etc.). This will affect how comparison values and goal comparisons are calculated and calculated.
-
-
Once you completed the Describe metric step, click the green Continue button to finish the Custom metric setup.
Additional Information
IN THIS SECTION
Integration Limitations
- Databox limits the use of its integrations to GET requests. This is because our integration only reads your data.
- Scopes: We use the following scopes: default
- Rate limits: No exact information is available in the API documentation.
- WARNING: If specific scopes of an integration allow you to create, change, delete or manipulate data in any other way, using such API calls can result in unexpected behavior. Databox is in no way liable for such API calls.